Tối ưu ngưỡng phát hiện phân tán cho hệ thống ra đa nhiều vị trí
321 lượt xemDOI:
https://doi.org/10.54939/1859-1043.j.mst.99.2024.12-23Từ khóa:
Ra đa nhiều vị trí; Phát hiện phân tán; Tối ưu hóa bầy đàn (PSO).Tóm tắt
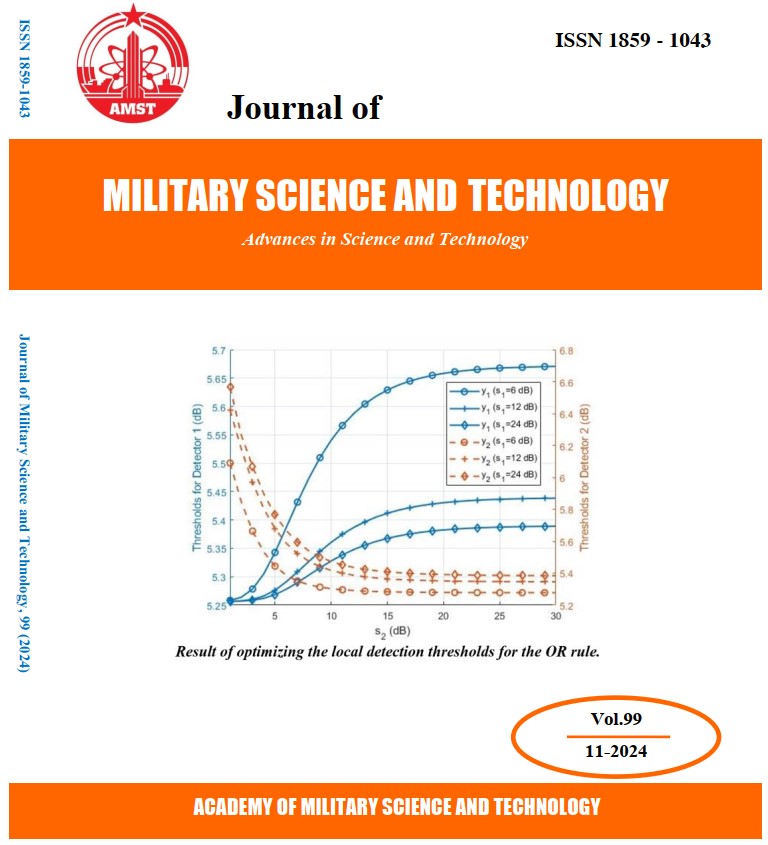
Trong bài báo này, chúng tôi đề xuất một phương pháp để tối ưu ngưỡng phát hiện phân tán cho hệ thống ra đa nhiều vị trí. Dưới tiêu chuẩn Neyman-Pearson, ngưỡng phát hiện thành phần được tối ưu sử dụng thuật toán tối ưu bầy đàn (PSO). Các mức ngưỡng thành phần được tối ưu để cực đại xác suất phát hiện tổng thể dưới sự ràng buộc của xác suất báo động lầm tổng thể cho trước. Ưu điểm của PSO là tính đơn giản, ít tham số và tìm kiếm toàn cục hiệu quả. Ví dụ mô phỏng số được đưa ra đối với trường hợp hệ thống ra đa gồm 2 trạm thành phần phát hiện phân tán đối với mục tiêu trong nhiễu Gauss độc lập thống kê. Các kết quả chỉ ra rằng, quy tắc hợp nhất OR luôn tối ưu và mức ngưỡng được xác định linh hoạt cho phép duy trì chất lượng phát hiện tổng thể khi có sự thay đổi không đồng nhất của tỉ số tín/nhiễu (SCR) ở mỗi trạm thành phần. Trong một số trường hợp, có thể bỏ qua việc tối ưu ngưỡng thành phần mà chất lượng phát hiện toàn hệ thống giảm không đáng kể.
Tài liệu tham khảo
[1]. Chernyak Victor S, “Fundamentals of multisite radar systems: multistatic radars and multiradar systems,” Routledge (2018). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203755228
[2]. E. Conte et al, “Multistatic radar detection: synthesis and comparison of optimum and suboptimum receivers,” IEE Proc. F - Commun., Radar and Signal Process., vol. 130, no. 6, pp. 484–494, (1983). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1049/ip-f-1.1983.0078
[3]. E. D’Addio et al: “Optimum and sub-optimum processors for multistatic radar systems,” in Riv. Tec. Selenia, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 21–28,, (1982).
[4]. R. Srinivasan, “Distributed radar detection theory,” IEE Proc. F - Commun., Radar and Signal Process., vol. 133, no. 1, pp. 55–60, (1986). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1049/ip-f-1.1986.0010
[5]. R. R. Tenney and N. R. Sandell, “Detection with distributed sensors,” IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst., vol. AES-17, no. 4, pp. 501–510, (1981). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TAES.1981.309178
[6]. Z. Chair and P. K. Varshney, “Optimal data fusion in multiple sensor detection systems,” IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst., vol. AES-22, no. 1, pp. 98–101, (1986). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TAES.1986.310699
[7]. I. Y. Hoballah and P. K. Varshney, “Neyman-Pearson detection with distributed sensors,” in Proc. 25th IEEE Conf. Decis. Control, vol. 25, pp. 237–241, (1986). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CDC.1986.267214
[8]. P. K. Varshney, “Distributed Detection and Data Fusion”. New York, NY, USA: Springer, (2012).
[9]. R. Viswanathan et al, “On counting rules in distributed detection,” IEEE Trans. Acoust., Speech, Signal Process., vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 772–775, (1989). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/29.17574
[10]. R. Niu and P. K. Varshney, “Distributed detection and fusion in a large wireless sensor network of random size,” EURASIP J. Wireless Commun. Netw., vol. 2005, no. 4, pp. 462–472, (2005). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/WCN.2005.462
[11]. R. Niu, P. K. Varshney, and Q. Cheng, “Distributed detection in a large wireless sensor network,” Inf. Fusion, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 380–394, (2006). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2005.06.003
[12]. V. Aalo et al, “On distributed detection with correlated sensors: two examples,” IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst., vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 414–421, (1989). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/7.30797
[13]. Nguyen Duc Minh, Bui Thi Dan, and Pham Van Hung, "The effect of correlated noise with student-t distribution to detection quality of distributed multi-location radar network", Journal of Military Science and Technology, vol. 56, pp. 68–75, (2018).
[14]. Nguyen Duc Minh, Bui Thi Dan, and Pham Van Hung, "To solve the problem of detection in multi-location radar network which affected by correlated noise with log-normal distribution model", Journal of Military Science and Technology, vol. 57, pp. 110–122, (2018).
[15]. Pham Van Hung and Nguyen Duc Minh, “The detection performance of the multistatic radar system with the copula-based dependence structure”, Journal of Science and Technology on Information and Communications, vol. 03, CS.01, pp. 124–130, (2020).
[16]. Pham Van Hung, Nguyen Duc Minh, and Nguyen Tuan Hung, “A new method solving the detection problem in distributed-processing multistatic radar system with statistically dependent local decisions”, Journal of Science and Technology on Information and Communications, vol. 01, CS.01, pp. 111–118, (2022).
[17]. Van Hung PHAM, Tuan Hung NGUYEN, Duc Minh NGUYEN, and Hisashi MORISHITA, “A New Method Based on Copula Theory for Evaluating Detection Performance of Distributed-Processing Multistatic Radar System”, IEICE Transactions on Communications, vol. E105-B, no. 1, pp. 67–75, (2022). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1587/transcom.2021EBP3001
[18]. Van Hung PHAM, Tuan Hung NGUYEN, and Hisashi MORISHITA, “Detection Performance Analysis of Distributed-Processing Multistatic Radar System with Different Multivariate Dependence Models in Local Decisions”, IEICE Transactions on Communications, vol. E105-B, no. 9, pp. 1097–1104, (2022). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1587/transcom.2021EBP3184
[19]. J. Kennedy and R. C. Eberhart, “Particle swarm optimization,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Neural Netw., Perth, Australia, vol. 4, pp. 1942–1948, (1995). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968
[20]. R. C. Eberhart and J. Kennedy, “A new optimizer using particle swarm theory,” in Proc. 6th Int. Symp. Micromachine Human Sci., Nagoya, Japan, pp. 39–43, (1995). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/MHS.1995.494215
[21]. S.-Y. Ho, H.-S. Lin, W.-H. Liauh, and S.-J. Ho, “OPSO: Orthogonal particle swarm optimization and its application to task assignment problems,” IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern. A, Syst., Humans, vol. 38, no. 2, pp. 288–298, (2008). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCA.2007.914796
[22]. B. Liu, L. Wang, and Y. H. Jin, “An effective PSO-based memetic algorithm for flow shop scheduling,” IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern. B, Cybern., vol. 37, no. 1 (2007), pp. 18–27. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2006.883272
[23]. G. Ciuprina, D. Ioan, and I. Munteanu, “Use of intelligent-particle swarm optimization in electromagnetics,” IEEE Trans. Magn., vol. 38, no. 2, pp. 1037–1040, (2002). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/20.996266
[24]. J. J. Liang, A. K. Qin, P. N. Suganthan, and S. Baskar, “Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer for global optimization of multimodal functions,” IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput., vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 281–295, (2006). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2005.857610